
Coccyx Pain (Coccygodynia)
The diagnosis and treatment of coccygodynia is an issue which has been discussed on for…
Joint cartilage problems constitute the frequently encountered patient group in orthopedic polyclinics since young ages. Among the most frequently seen joint problems are knee front pain, partial cartilage loss, joint cartilage damage and age-dependent cartilage damage. Problems such as strong pain and restriction of movement ability which are caused by joint problems could significantly decrease the life quality of the patient. Hopefully, the patients could be provided with a quality life due to the treatment methods of today.
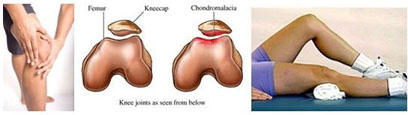
1. Anterior Knee pain: The most frequently seen problem related to joints is the anterior knee pain. This is most frequently seen in persons aged 25- 45, working on the desk and have no regular sports habit. Anterior knee pain is expressed as “Chondromalacia Patella”, which develops as a result of the softening of patella cartilage. If there is not structural disorder, this most frequently arises as a result of weakness of thigh front muscle group. This could lead to loss of cartilage in the long run if not properly treated. It could mostly be treated with muscle strengthening exercises.
2. Partial cartilage defect: This joint damage which is seen with second highest frequency mostly 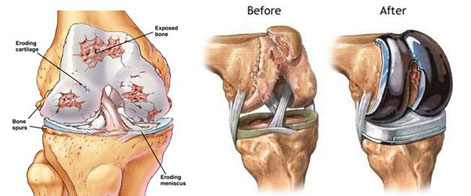 occurs during contests or trainings. In case of partial cartilage loss, which mostly requires surgical treatment, different methods are applied depending on the size and place of the damaged area. New methods are added with the development of medical technologies to these methods that accomplish high rate success. Among these methods which are successfully applied is the reproduction in the laboratory of the cartilage cell received from the person through cartilage culture and transferring the same to the damaged area. Another methods which is currently being developed is to obtain cartilage from stem cell, which currently being worked on globally and in our country. The purpose in this study is to access the original and permanent cartilage.
occurs during contests or trainings. In case of partial cartilage loss, which mostly requires surgical treatment, different methods are applied depending on the size and place of the damaged area. New methods are added with the development of medical technologies to these methods that accomplish high rate success. Among these methods which are successfully applied is the reproduction in the laboratory of the cartilage cell received from the person through cartilage culture and transferring the same to the damaged area. Another methods which is currently being developed is to obtain cartilage from stem cell, which currently being worked on globally and in our country. The purpose in this study is to access the original and permanent cartilage.
3. Widespread damage of joint cartilage (Arthrosis):
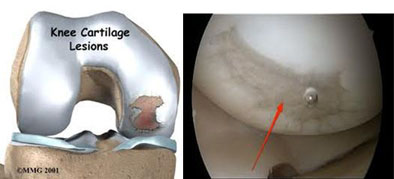 This is the third widespread cartilage problem in joints that is due to aging. Widespread cartilage damage generally occurs in patients over 60 as the cartilage thickness get thin due to physiological aging. This problem, which has the medical name “arthrosis”, is known as calcification among public. In patients above 60 years of age, methods which decrease pain and increase movement ability could be preferred. The purpose of the treatment is to help the patient to keep his/her own joint as long as possible, thus enabling a pain-free and quality life. Physical treatment methods which have been applied throughout the years are various rescuing and supportive surgical treatment methods, in-joint synthetic joint fluid injection methods, medication and partial joint prosthesis, which carry the total prosthesis application age of the patient to advanced ages. However, the impact period of each method is limited. For joints where the arthrosis is at a developed stage, it is required to eventually apply total joint prosthesis. However, even in this method, the life of the prosthesis to be placed despite the medical technology of today, does not exceed 20 years.
This is the third widespread cartilage problem in joints that is due to aging. Widespread cartilage damage generally occurs in patients over 60 as the cartilage thickness get thin due to physiological aging. This problem, which has the medical name “arthrosis”, is known as calcification among public. In patients above 60 years of age, methods which decrease pain and increase movement ability could be preferred. The purpose of the treatment is to help the patient to keep his/her own joint as long as possible, thus enabling a pain-free and quality life. Physical treatment methods which have been applied throughout the years are various rescuing and supportive surgical treatment methods, in-joint synthetic joint fluid injection methods, medication and partial joint prosthesis, which carry the total prosthesis application age of the patient to advanced ages. However, the impact period of each method is limited. For joints where the arthrosis is at a developed stage, it is required to eventually apply total joint prosthesis. However, even in this method, the life of the prosthesis to be placed despite the medical technology of today, does not exceed 20 years.
Latest Trends Frequently used in Joint Treatments
 1.Food additives increase the movement ability: Cartilage supportive products, which contain glucosamine and condroitin and abundantly found in the market under the name food additives, are among the most common methods of treatment today. These products, which are totally obtained from natural substances, provides benefit in 60 percent of the patients with widespread cartilage damage, mitigates pain and increases the movement ability. The only side effect of these products is that they increase blood sugar in patients with diabetes. For that reason, they are not recommended to be used in diabetic patients.
1.Food additives increase the movement ability: Cartilage supportive products, which contain glucosamine and condroitin and abundantly found in the market under the name food additives, are among the most common methods of treatment today. These products, which are totally obtained from natural substances, provides benefit in 60 percent of the patients with widespread cartilage damage, mitigates pain and increases the movement ability. The only side effect of these products is that they increase blood sugar in patients with diabetes. For that reason, they are not recommended to be used in diabetic patients.
2. Plasma treatment alleviates pain and swelling episodes: PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) is used for improving tendon and links in orthopedics. Besides, it is applied as a very new method in the treatment of widespread joint cartilage damages. In PRP treatment, the blood amounting 20- 50 cc obtained from the person, is distilled by means of a special tool within a couple of minutes without putting any additive in it. From this blood, a rich plasma is obtained which includes intense improving and edema mitigating factors at an amount of 5- 7 cc, and it is injected to the damaged joint. When the method is repeated several times, the pain and swelling episodes that occur due to arthrosis is mitigated. By this means, the age of applying prosthesis is advanced, providing the patient with a couple of years.
3. Application of cartilage cell culture provides original cartilage to young patients: The cartilage cell which is obtained from the person is replicated under laboratory environment and transformed to the damaged area with operation. Despite the fact that is a a more expensive method compared to other methods in terms of cost, the cartilage which is produced is the original joint cartilage and does not required taking cartilage from another part of the body, so the patient feels less paint after the operation.
4. Joints are renewed with arthroplasty: Arthroplasty is the general name of the process wherein partial or full prosthesis is applied as the distorted surface of the joint is removed. In cases where the joint looses its function totally, the method of replacing the whole joint (total joint arthroplasty) is used. In recent years, partial surface replacement prosthesis, which was previously only used for damaged area in case of partial damage in joints in elderly patients, has been started to be widely used. The advantage of these partial prosthesis: Since it is applied by cutting the joint bone is slightly with minor surgical cuts, the operation period and healing period is short, without constituting any obstacle for the total joint prosthesis that could be required in the future. Patients could return back to normal pain-free daily life in a short period of time with these methods.