What İs the treatment of articular cartilage damage?
Joint cartilage problems constitute the frequently encountered patient group in orthopedic polyclinics since young ages.…

What is knee prosthesis?
It is the process of replacing the knee joint which is distorted due to various reasons, with artificial joint made of metal under operation.
In young people:
-Congenital diseases of the knee joint
-Knee joint infection that happened during childhood (septic arthritis)
-In the aftermath of untreated in-joint fractures
-Osteonecrosis disease
-In the aftermath of rheumatism diseases
-In the aftermath of metabolic diseases (such as gout)
-In the aftermath of frequent in-joint bleedings due to hemophilia disease
In the advanced ages:
-It develops in particular due to old age after 65
-Obesity (excessive weight)
-Knee prosthesis may be required due to rheumatic diseases
When should the knee prosthesis be applied?
There are 2 important justifications for knee prosthesis operation due to calcification,
1-The walking distance of the patient falling below 300 meters, or
2-The patient being required to use pain killing drugs every day, in case of the occurrence of these, it is time to apply prosthesis to the patient. Kidney and liver damage due to drugs could occur in patients who are required to take pain killers every day.
It is beneficial use apply prosthesis for increasing the walking distance of the patient and avoiding the need for pain killers. 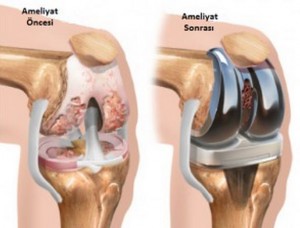
For Whom Knee Prosthesis is not Applicable?
-Prosthesis is not applied to patients who have active infection focus in the body until the infection is cured
Does Knee Prosthesis Have Any Alternative?
Joint fusion surgery could be performed in addition to prosthesis in patients who have difficulty in walking and have strong pain due to failure of knee joint. Joint fusion surgery is preferred in persons who perform heavy physical work. However, if both knee joints are distorted, it is undesirable to perform fusion operation for both knees. Joint fusion operation has gradually been decreased since it leads to restriction of movement at an advanced level. People prefer movable knee joint instead of frozen knee joint.
Viscosupplementation (artificial joint fluid injection): Injections made inside the joint in knee joint damege are not an alternative to prosthesis, they only extend the period required for applying the prosthesis, thus granting time to the patient.
Glucosamines and type 2 collagens: These substances are sold in the market. These have the impact of slowing down the cartridge wearing and repairing some damage. However, these only delay the prosthesis surgery in widespread joint surface damage. These do not protect the patient from undergoing a surgery.
Physical Treatment: Although this has benefits in strengthening the muscles around the knee and temporarily alleviating the pain, these do not stop joint surface damage, save the patient from operation, but only grant time.
Using Knee Support: This may decrease the loading on knee joint and mitigate pain, however do not prevent joint surface damage, and only grant time.
Arthroscopic Knee Cleaning: It does not prevent damage; cleaning is only performed inside the joint and may grant time to the person by mitigating the pain.
High Tibial Osteotomies: This could be preferred in patients aged 50 – 60 who have damage in single joint interval due to angular deformity. The bone is cut off and the load is provided to fall on the health joint surface and thus the pain could be mitigated. However, certain criteria should be met for the surgery. It is not applied to all patients.
What are the Types of Prosthesis ?
Knee prosthesis are divided into two groups being total knee prosthesis and unicondular(partial) knee prosthesis .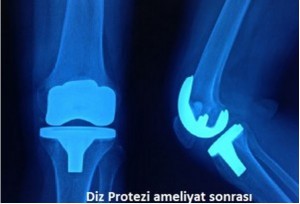
In total 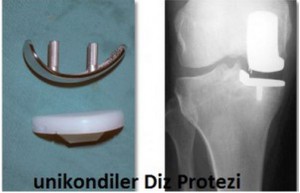 knee prosthesis, both internal (medial and lateral)surfaces of the knee joint are replaced. Total knee prosthesis has 2 types, which cut off and protect the posterior cruciate ligament. The orthopedic surgeon who assesses the patient decides on which type of prosthesis is to be used for the patient.
knee prosthesis, both internal (medial and lateral)surfaces of the knee joint are replaced. Total knee prosthesis has 2 types, which cut off and protect the posterior cruciate ligament. The orthopedic surgeon who assesses the patient decides on which type of prosthesis is to be used for the patient.
In unicondular knee prosthesis, the internal(medial or lateral) joint surface of the knee are replaced. The purpose of this prosthesis is to provide the patient with time until total knee prosthesis is performed. However, there are strict rules for applying unicondular knee prosthesis (The patient being young, having a weight under 85 kg and having only one single knee surface distortion). Number of patients fitting these rules is quite limited.  For that reason, it is performed at very low numbers compared to total knee prosthesis.
For that reason, it is performed at very low numbers compared to total knee prosthesis.
In addition to arthrosis (joint surface damage), there are Special Tumor Prosthesis when it is required to remove the bone following bone tumor surgeries.
What is the Process of Surgery?
Before all prosthesis surgeries, the patients should be examined from top to bottom and it should be searched whether there is any infection focus on the body. For that reason, blood and urine tests are performed on all of our patients before the surgery, and the patient is prepared to surgery after it is seen that the results are clean. At this stage, in patients who take anticoagulant medication, the drug is stopped 5 to 10 days prior to the operation depending on the nature of the drug, replacing with short impact anticoagulant injections (heparin with low molecule weight). When the risk of bleeding stops a couple of days before the operation, the patient could restore to the former routine treatment. It could be necessary to transfuse blood to the patient in case of surgeries with bleeding. Prosthesis operations should be performed in operation rooms having special ventilation. Standard operation rooms are not suitable for knee prosthesis.
The patient is mobiles and walked within 12 hours following the operation.
The patient is walked every 2-3 hours during the period of hospitalization. This is the most effective way to prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis that could occur. Besides, heparin injection with low molecule weight is applied subcutaneously to the patient. Tablet is applied instead of anticoagulant injection during discharge. The patient is requested to take anticoagulant pills for 30 days.
What are the possible complications during and after the operation?
During knee prosthesis operation, problems such as vein – nerve injury and fracture on the bone could occur. Early and late complications could develop after the operation.
Early complications: Prosthesis infection, deep veine thrombosis, wound problem
Late complications: Pain and early loosening of prosthesis. These complications could be minimized by taking relevant measures, however, it is not possible to totally avoid them.
The average life of total knee prosthesis ranges between 15 to 20 years. However, there are prosthesis which last up to 25 years. The life of prosthesis could change depending on the surgery technique, type of the prosthesis applied, activity level and bone quality of the patient, as well as his body weight.
What should be done to protect against infections following prosthesis surgery?
The patient who has prosthesis in his body has the risk of getting infected throughout the life. Patients with prosthesis should take protective antibiotics before any surgical intervention, including tooth extraction or filling.